Nutrition ecology: ensuring plant products quality

Abstract
The health of the nation largely depends on the socio-economic and living conditions of a person, including the ecology of nutrition. In modern conditions, the environmental purity of food is becoming an increasingly important global problem, which not only concerns people’s health, but also has a significant impact on the economies of countries. Vegetables play an important role in human nutrition. They are natural medicinal and prophylactic agents and contain physiologically active substances, vitamins, minerals, organic acids, fiber. When organizing greenhouse plant production, which can give products throughout a year, it is necessary to consider the conception of a modern policy in the field of healthy nutrition of the population which provides for obtaining crop products in environmentally optimal conditions. The purpose of the research was the development of innovative technical solutions aimed at ensuring the quality of greenhouse crop products. The object of the research is agro-technologies of hydroponic vegetable cultivation; the subject of the research is the impact of agricultural practices associated with biological plant protection and plant diagnostics on crop yield and product quality. The working hypothesis is formulated as follows: the use of promising methods of plant protection and plant diagnostics can increase crop yields and ensure the quality of crop products. As a result of theoretical and experimental studies, the technology of A. colemani mass production for the biological protection of cucumber plants has been improved; a technique for identifying the stress state of plants, that does not require sample preparation and based on the evaluation of the leaf apparatus absorption spectra, has been developed. The analysis of the obtained results showed the economic and energy efficiency of the presented technical solutions. The use of biological methods for plant protection and plant diagnostics helped to increase crop yields and to ensure the quality of crop products.
Table of Contents:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology
4. Empirical Findings
5. Conclusions
1. Introduction
The health of a nation is known to depend on the socio-economic and living conditions of a person, including the nutrition ecology, by 52 ... 55% (Food safety and main criteria for its assessment, 2018), (Blednykh, 2003), (About fundamental principles of the Russian Federation state policy in the sphere of healthy nutrition of the population for the period up to 2020, 2010). Nutrition, as a social criterion, is one of the most important factors determining the health of the population: high-quality, balanced diets help to prevent diseases and to increase working efficiency, to ensure child’s appropriate growth and development. In this regard, the ecological purity of food is becoming an increasingly important global problem which not only concerns people’s health, but also has a significant impact on the economies of countries. (Food safety and main criteria for its assessment, 2018), (Blednykh, 2003), (About fundamental principles of the Russian Federation state policy in the sphere of healthy nutrition of the population for the period up to 2020, 2010).
The article deals with the issues related to nutrition ecology; the research purpose is the development of innovative technical solutions aimed at ensuring the quality of greenhouse crop products.
The object of the research is agro-technologies of hydroponic vegetable cultivation; the subject of the research is the impact of agricultural practices associated with biological plant protection and plant diagnostics on crop yield and product quality. The working hypothesis is formulated as follows: the use of promising methods of plant protection and plant diagnostics can increase crop yields and ensure the quality of crop products.
2. Literature Review
The ecological purity of food is of particular importance in the current conditions of increasing anthropogenic pressure on the environment (Bantis, et al., 2018), (Kraska, Kleinschmidt, Weinand, & Pude, 2018), (Rouphael, Kyriacou, Petropoulos, De Pascale, & Colla, 2018), (Ku, et al., 2018), (Nay-Htoon, et al., 2018), (Saha, Mandal, & Dutta, 2018), (Bianciotto, Victorino, Scariot, & Berruti, 2018), (Lisetskii, 2018), (Belachew, Nagel, Fiorani, & Stoddard, 2018), (Wang, et al., 2018), (Kumar, Singh, & Adholeya, 2017), (Gautam & Fomsgaard, 2017), ( Salazar-Moreno, et al., 2017), (Miranda, Lara, Rocksch, Dannehl, & Schmidt, 2017), (Prasad, Bhattacharyya, & Nguyen, 2017), (Zhang, Wijesundara, Abbey, & Rupasinghe, 2017), (Yi, et al., 2017). Continuous pollution of nature creates a source of dangerous eco-toxicants that get into food raw materials and then into food products which have the ability to accumulate some of them. Therefore, 40 ... 50% of substances- pollutants enter the human body with food from the environment, 20 ...40% of them enter with water (Food safety and main criteria for its assessment, 2018), (Blednykh, 2003), (About fundamental principles of the Russian Federation state policy in the sphere of healthy nutrition of the population for the period up to 2020, 2010).
A contemporary conception in the field of healthy nutrition provides for the expansion of domestic manufacturing the main types of food raw materials that meet the requirements of safety and quality (Blednykh, 2003). Food products should satisfy the physiological needs of human body in vital substances, as well as perform therapeutic and environmental preventive tasks (Belogubova, Vasiliev, & Gil, 2007).
Vegetables play an important role in human nutrition because they contain a number of physiologically active substances, which take part in all metabolic processes, serve as a source of vitamins, contained a balanced complex of mineral substances, organic acids and fiber. In the conditions of intensified impact of adverse factors on human body, vegetables contribute to good health promotion; they are natural medicinal and prophylactic agents. Fresh vegetables are of great value, since a number of biologically active substances lose their properties during heat treatment (Belogubova, Vasiliev, & Gil, 2007).
The possibility of consuming fresh vegetables is limited to the season of the year. Therefore, a year-round manufacturing crop products under greenhouses conditions is one of the possible ways to solve this problem (Belogubova, Vasiliev, & Gil, 2007), (Autko, Ganush, & Dolbik, 2006).
When organizing greenhouses, it is necessary to take into account that vegetable products grown without effective plant protection and plant diagnostics are not competitive in the world market. In addition, food quality requirements are constantly rising; and the absence of residues belonging to chemical protection means as well as the content of other ecotoxicants conformed to standards (Belogubova, Vasiliev, & Gil, 2007) (Shpaar, Bakkhauz, Baton, Belyakova, & Burt, 2005) are of paramount importance.
3. Methodology
Experimental studies were carried out in the Limited Liability Company Agrocomplex “Churilovo”, Chelyabinsk city. The cultivation method is a photoculture (low-volume aggregate-ponics); the cultivated crop is a medium sized cucumber F1 “Meva”. The chemical composition of cucumber fruit was determined in Federal Budgetary Institution of Health Care “Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the Chelyabinsk Region”. Plant diagnostics involved the analysis of leaf apparatus absorption spectra using photometric equipment: UV 1800 Shimadzu spectrophotometer, a LASA AGRO 2800 laboratory. The variational statistics methods were used to evaluate the results obtained.
Plant protection was carried out using a biological method, the advantages of which include cumulative effect, reduction or rejection of using the chemical means for plant protection, sparing environmental impact, protection of plants cultivated for child nutrition, etc. (Shpaar, Backhouse, Baton, Belyakova, & Burt, 2005). An energy- and resource- saving technology involving the use of an organic-mineral substrate was developed for aphidophidus entomophage (A. colemani) mass cultivation in the LLC Agrocomplex “Churilovo”.
A technique developed at the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education “South Ural State Agrarian University” was used to diagnose the plants state. It is intended for the production conditions of greenhouse farms; it does not require sample preparation and can detect stress states based on leaf apparatus absorption spectra before carrying out the corresponding chemical analysis (Belogubova, Vasiliev, & Gil, 2007).
4. Empirical Findings
As a result of theoretical and experimental studies, the technology of Aphidius colemani mass production for the biological protection of cucumber plants has been improved. According to this technology the number of basic operations related to the preparation of the substrate has been reduced; and the number of components included in its composition has been decreased. The main difference of this technology is the use of ultrasonic processing of the substrate organic part which activates the interaction of the chain links “substrate - fodder plant - phytophage - entomophage” (Basarygina, Putilova, & Panova, Eco-module: biological plant protection, 2015). The use of the proposed organic-mineral substrate consisting of peat and mineral wool helps not only to increase the number of entomophages during the cultivation period, but also to ensure their guaranteed departure at the application stage (by attaching mobile lawns with entomophages to the irrigation system of protected plants). Such technological technique is not possible to use for all other known substrates, since there is no mineral wool foundation in their composition.
This leads to deteriorating the properties of vegetable root environment.
The calculation results of economic and energy efficiency when using agrotechnologies for greenhouse vegetable cultivation are given in Table 1.
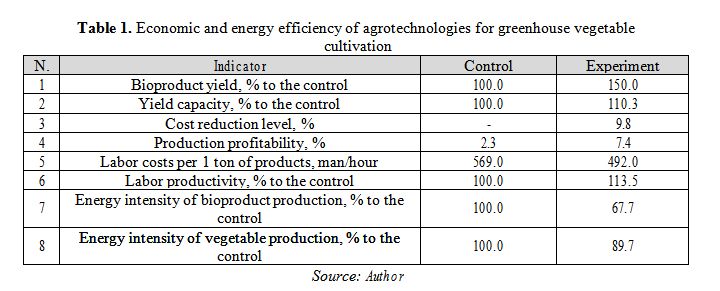
The analysis of presented results shows that the improved method of Aphidius colemani mass production for biological protection of cucumber plants proved to be profitable in terms of energy and economy. In the experimental variant the bioproduct yield increases by 50%, and the cucumber yield increases by 10.3%. We may observe growing production profitability and labor productivity and decreasing cost of production. The energy intensity of vegetable production is reduced by 10.3%, the energy intensity of Aphidius colemani production is reduced by 33.3%.
The developed technique for diagnosing the plant state included:
- determining the absorption spectra of leaf apparatus of vegetable plants,
- comparing the obtained absorption spectra with the recommended ones;
- correcting the nutrition regimen of vegetable plants.
The nutrition regimen was corrected in the case, when significant differences between the obtained absorption spectra and those recommended were detected in accordance with the scheme (Fig. 1). The main maxima and pigment absorption areas were taken from the data of known publications (Basarygina, Gorshkova, & Putilova, 2016).
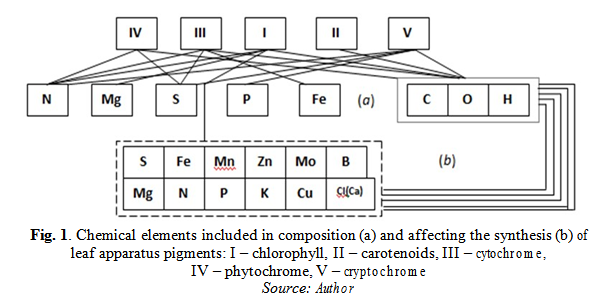
Particularly, when identifying significant differences in the values of chlorophyll absorption according to the results of processing experimental data (using Student’s criterion), special attention was paid to such nutrients as magnesium and iron, as well as sulfur, manganese, molybdenum, zinc and boron (Fig. 1). The supply of leaf apparatus by nutritious elements and the composition of root environment were determined by means of chemical analysis.
The research results of cucumber fruits quality (% by wet weight) are shown in table 2. The nitrate content was 100 mg/kg; pesticides were not found.
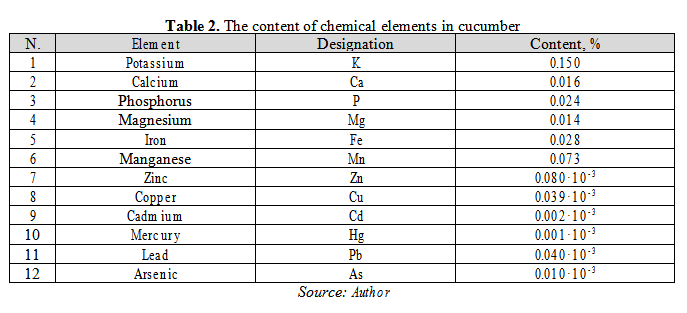
The analysis of these data reveals that the content of Eco toxicants in cucumber fruits is below the maximum permissible concentrations; the content of nutritional elements is in accordance with the established standards.
Thus, the use of biological methods of plant protection and plant diagnostics can increase the yields and ensure the quality of crop products.
The presented technical solutions are recommended for usage in greenhouse vegetable cultivation technologies. The field of further research relates to the improvement of Phyto monitoring methods which can (due to the timely detection of plants stress states) ensure the high quality of crop products.
5. Conclusions
Ecological purity of food products is of importance in modern conditions, since the pollution of the environment results in the formation of a source of hazardous Eco toxicants that get into food. Vegetables play an important role in human nutrition; they contain physiologically active substances, vitamins, mineral substances, organic acids, fiber; they are natural medicinal and prophylactic agents. The most valuable are fresh, raw vegetables, but the possibility of consuming fresh vegetables is limited to the season of the year.
When organizing a greenhouse crop production, which makes it possible to receive vegetable products throughout a year, it is necessary to consider the conception of a contemporary policy in the field of healthy nutrition of the population which provides for obtaining crop products in environmentally optimal conditions. In this regard, the urgent task is to ensure the quality of crop products.
The purpose of the conducted research was the development of innovative technical solutions aimed at ensuring the quality of greenhouse vegetable products.
As a result of theoretical and experimental studies the technology of A. Coleman mass production for the biological protection of cucumber plants has been improved; a technique for identifying the stress state of plants has been developed. It does not require sample preparation, and it is based on the evaluation of leaf apparatus absorption spectra.
The analysis of the obtained results confirmed the stated hypothesis and showed the economy and energy efficiency of the presented technical solutions. The use of biological methods for plant protection and plant diagnostics contributes to increasing yields and ensuring the quality of crop products.
The Authors:
BASARYGINA E.M. [1]
SHERSHNEV A.V. [1]
PUTILOVA T.A. [2]
[1] FSBEI HE “South Ural State Agrarian University”, Troitsk (RUSSIA).
[2] FSBEI HE “South Ural State Humanitarian Pedagogical University”, Chelyabinsk (RUSSIA).
Contributo selezionato da Filodiritto tra quelli pubblicati nei Proceedings “Ecological Agriculture and Sustainable Development - 2019”
Per acquistare i Proceedings clicca qui.
Contribution selected by Filodiritto among those published in the Proceedings “Ecological Agriculture and Sustainable Development - 2019”
To buy the Proceedings click here.



